Publications
Group highlights
Hoang Trieu Vy Le, Marion Foare, Nelly Pustelnik
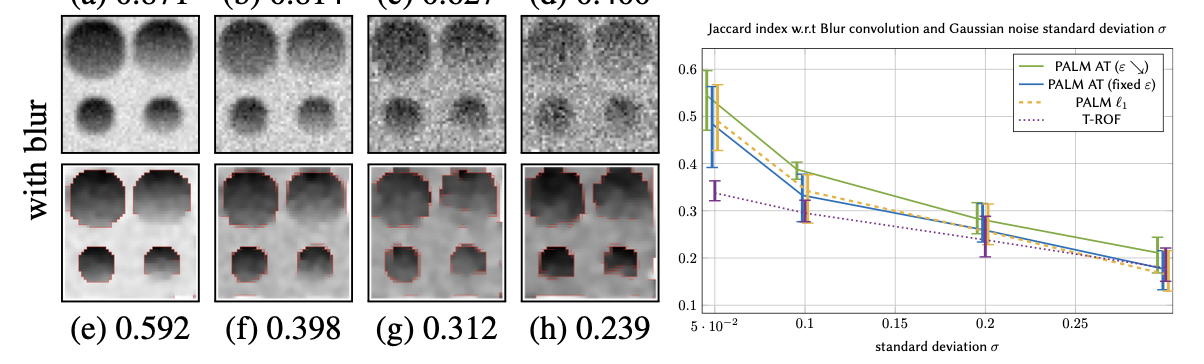
This work is dedicated to joint image restoration and contour detection considering the Ambrosio-Tortorelli functional. Two proximal alternating minimization schemes with convergence guarantees are provided, PALM-AT and SL-PAM-AT, as well as closed-form expressions of the involved proximity operators. A thorough numerical study is conducted in order to evaluate the performance of both numerical schemes as well as comparisons to state-of-the-art Mumford-Shah strategies.
C.G. Lucas, B. Pascal, N. Pustelnik, and P. Abry

This work focuses on a parameter-free joint piecewise smooth image denoising and contour detection. Formulated as the minimization of a discrete Mumford-Shah functional and estimated via a theoretically grounded alternating minimization scheme, the bottleneck of such a variational approach lies in the need to fine-tune their hyperparameters, while not having access to ground truth data. To that aim, a Stein-like strategy providing optimal hyperparameters is designed, based on the minimization of an unbiased estimate of the quadratic risk. Efficient and automated minimization of the estimate of the risk crucially relies on an unbiased estimate of the gradient of the risk with respect to hyperparameters. Its practical implementation is performed using a forward differentiation of the alternating scheme minimizing the Mumford-Shah functional, requiring exact differentiation of the proximity operators involved. Intensive numerical experiments are performed on synthetic images with different geometry and noise levels, assessing the accuracy and the robustness of the proposed procedure. The resulting parameter-free piecewise-smooth estimation and contour detection procedure, not requiring prior image processing expertise nor annotated data, can then be applied to real-world images.
Signal, Image and Video Processing, pp.1-8, Dec. 2022.
L. M. Briceño-Arias and N. Pustelnik
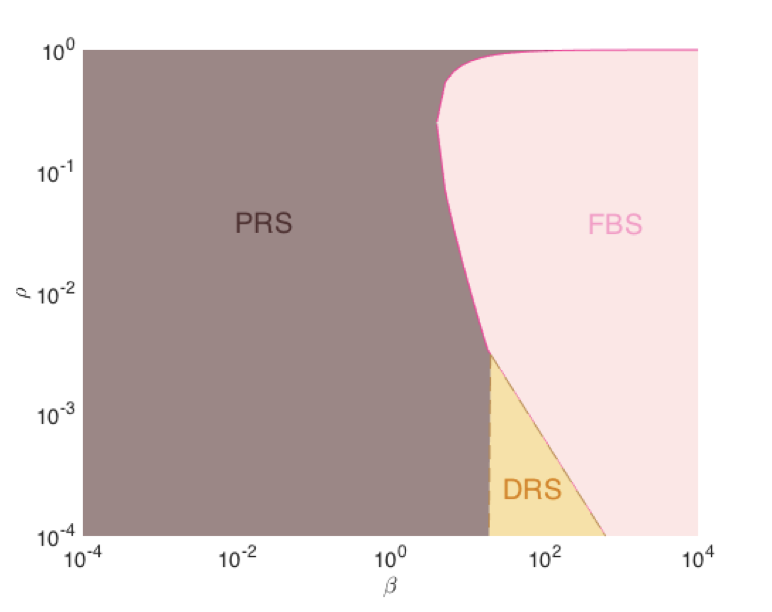
In this paper we provide a theoretical and numerical comparison of convergence rates of forward-backward, Douglas-Rachford, and Peaceman-Rachford algorithms for minimizing the sum of a convex proper lower semicontinuous function and a strongly convex differentiable function with Lipschitz continuous gradient. Our results extend the comparison made in [1], when both functions are smooth, to the context where only one is assumed differentiable. Optimal step-sizes and rates of the three algorithms are compared theoretically and numerically in the context of texture segmentation problem, obtaining very sharp estimations and illustrating the high efficiency of Peaceman-Rachford splitting.
L.M. Briceño-Arias and N. Pustelnik
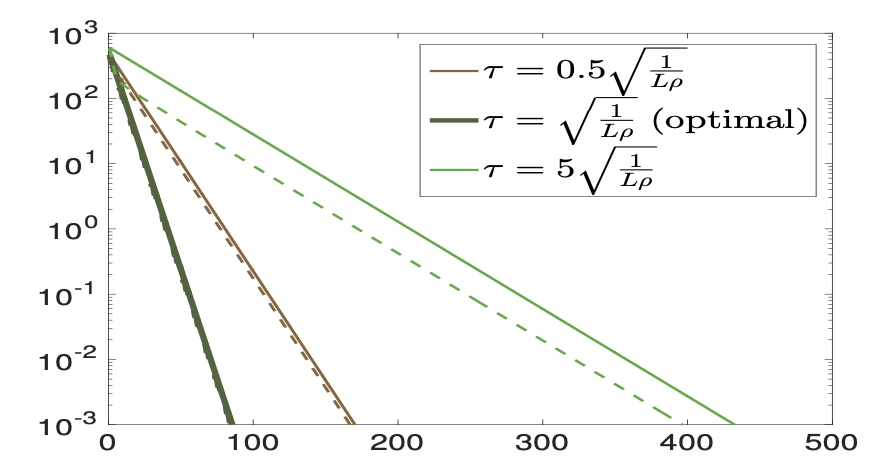
In this paper we provide a theoretical and numerical comparison of convergence rates of forward-backward, Douglas-Rachford, and Peaceman-Rachford algorithms for minimizing the sum of a convex proper lower semicontinuous function and a strongly convex differentiable function with Lipschitz continuous gradient. Our results extend the comparison made in [1], when both functions are smooth, to the context where only one is assumed differentiable. Optimal step-sizes and rates of the three algorithms are compared theoretically and numerically in the context of texture segmentation problem, obtaining very sharp estimations and illustrating the high efficiency of Peaceman-Rachford splitting.
B. Pascal, S. Vaiter, N. Pustelnik, and P. Abry
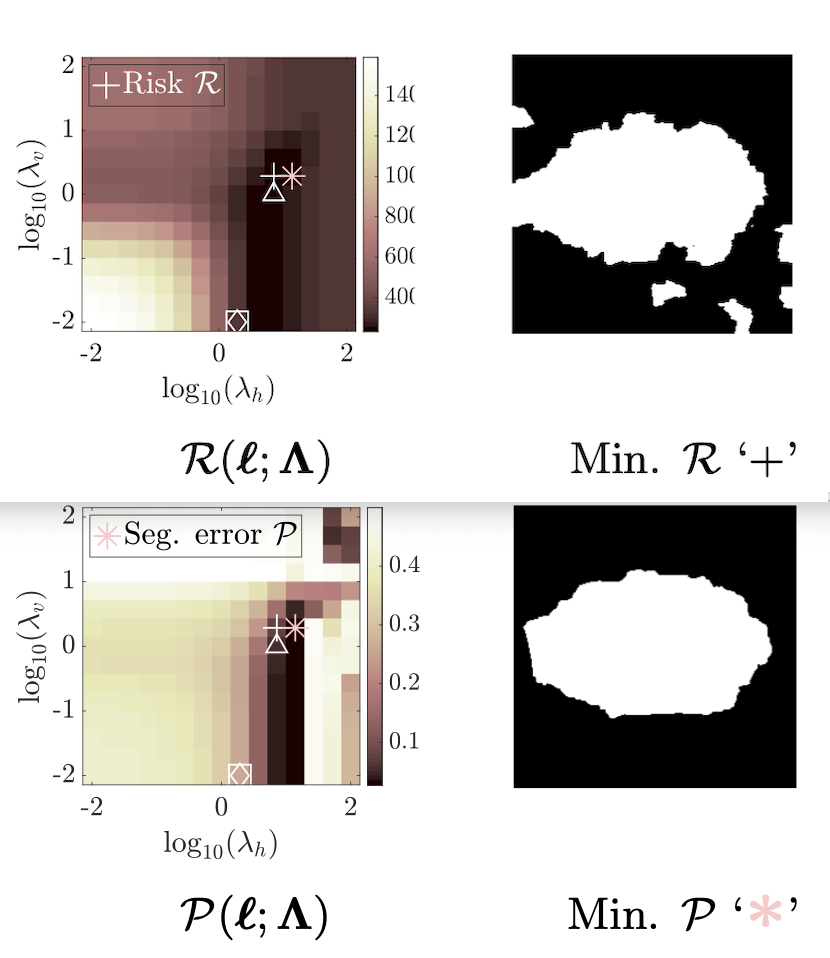
Penalized Least Squares are widely used in signal and image processing. Yet, it suffers from a major limitation since it requires fine-tuning of the regularization parameters. Under assumptions on the noise probability distribution, Stein-based approaches provide unbiased estimator of the quadratic risk. The Generalized Stein Unbiased Risk Estimator is revisited to handle correlated Gaussian noise without requiring to invert the covariance matrix. Then, in order to avoid expansive grid search, it is necessary to design algorithmic scheme minimizing the quadratic risk with respect to regularization parameters. This work extends the Stein’s Unbiased GrAdient estimator of the Risk of Deledalle et al. to the case of correlated Gaussian noise, deriving a general automatic tuning of regularization parameters. First, the theoretical asymptotic unbiasedness of the gradient estimator is demonstrated in the case of general correlated Gaussian noise. Then, the proposed parameter selection strategy is particularized to fractal texture segmentation, where problem formulation naturally entails inter-scale and spatially correlated noise. Numerical assessment is provided, as well as discussion of the practical issues.
B. Pascal, N. Pustelnik, and P. Abry
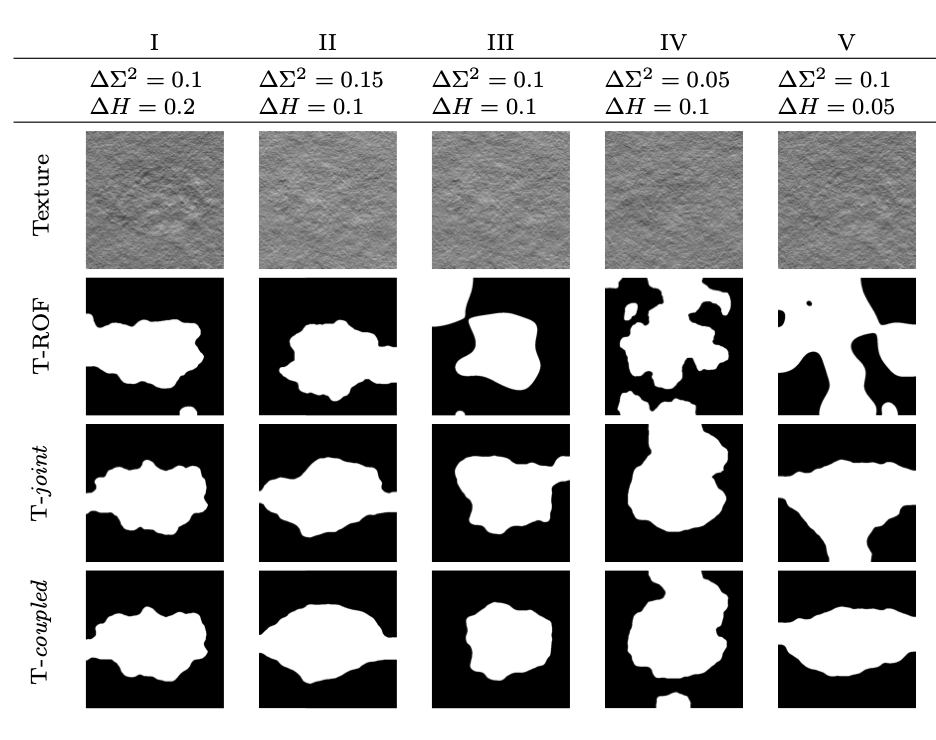
The present work investigates the segmentation of textures by formulating it as a strongly convex optimization problem, aiming to favor piecewise constancy of fractal features (local variance and local regularity) widely used to model real-world textures in numerous applications very different in nature. Two objective functions combining these two features are compared, referred to as joint and coupled, promoting either independent or co-localized changes in local variance and regularity. To solve the resulting convex nonsmooth optimization problems, because the processing of large size images and databases are targeted, two categories of proximal algorithms (dual forward-backward and primal-dual), are devised and compared. An in-depth study of the objective functions, notably of their strong convexity, memory and computational costs, permits to propose significantly accelerated algorithms. A class of synthetic models of piecewise fractal texture is constructed and studied. They enable, by means of large-scale Monte-Carlo simulations, to quantify the benefits in texture segmentation of combining local regularity and local variance (as opposed to regularity only) while using strong-convexity accelerated primal-dual algorithms. Achieved results also permit to discuss the gains/costs in imposing co-localizations of changes in local regularity and local variance in the problem formulation. Finally, the potential of the proposed approaches is illustrated on real-world textures taken from a publicly available and documented database.
M. Jiu and N. Pustelnik

Image restoration remains a challenging task in image processing. Numerous methods tackle this problem, often solved by minimizing a non-smooth penalized co-log-likelihood function. Although the solution is easily interpretable with theoretic guarantees, its estimation relies on an optimization process that can take time. Considering the research effort in deep learning for image classification and segmentation, this class of methods offers a serious alternative to perform image restoration but stays challenging to solve inverse problems. In this work, we design a deep network, named DeepPDNet, built from primal-dual proximal iterations associated with the minimization of a standard penalized likelihood with an analysis prior, allowing us to take advantage of both worlds. We reformulate a specific instance of the Condat-Vu primal-dual hybrid gradient (PDHG) algorithm as a deep network with fixed layers. The learned parameters are both the PDHG algorithm step-sizes and the analysis linear operator involved in the penalization (including the regularization parameter). These parameters are allowed to vary from a layer to another one. Two different learning strategies “Full learning” and “Partial learning” are proposed, the first one is the most efficient numerically while the second one relies on standard constraints ensuring convergence in the standard PDHG iterations. Moreover, global and local sparse analysis prior are studied to seek a better feature representation. We apply the proposed methods to image restoration on the MNIST and BSD68 datasets and to single image super-resolution on the BSD100 and SET14 datasets. Extensive results show that the proposed DeepPDNet demonstrates excellent performance on the MNIST and the more complex BSD68, BSD100, and SET14 datasets for image restoration and single image super-resolution task
B. Pascal, N. Pustelnik, P. Abry, J.-C. Géminard , V. Vidal
Numerous fields of nonlinear physics, very different in nature, produce signals and images, that share the common feature of being essentially constituted of piecewise homogeneous phases. Analyzing signals and images from corresponding experiments to construct relevant physical interpretations thus often requires detecting such phases and estimating accurately their characteristics (borders, feature differences, …). However, situations of physical relevance often comes with low to very low signal to noise ratio precluding the standard use of classical linear filtering for analysis and denoising and thus calling for the design of advanced nonlinear signal/image filtering techniques. Additionally, when dealing with experimental physics signals/images, a second limitation is the large amount of data that need to be analyzed to yield accurate and relevant conclusions requiring the design of fast algorithms. The present work proposes a unified signal/image nonlinear filtering procedure, with fast algorithms and a data-driven automated hyperparameter tuning, based on proximal algorithms and Stein unbiased estimator principles. The interest and potential of these tools are illustrated at work on low-confinement solid friction signals and porous media multiphase flows.
M. Foare, N. Pustelnik, and L. Condat

The Mumford-Shah model is a standard model in image segmentation, and due to its difficulty, many approximations have been proposed. The major interest of this functional is to enable joint image restoration and contour detection. In this work, we propose a general formulation of the discrete counterpart of the Mumford-Shah functional, adapted to nonsmooth penalizations, fitting the assumptions required by the Proximal Alternating Linearized Minimization (PALM), with convergence guarantees. A second contribution aims to relax some assumptions on the involved functionals and derive a novel Semi-Linearized Proximal Alternated Minimization (SL-PAM) algorithm, with proved convergence. We compare the performances of the algorithm with several nonsmooth penalizations, for Gaussian and Poisson denoising, image restoration and RGB-color denoising. We compare the results with state-of-the-art convex relaxations of the Mumford-Shah functional, and a discrete version of the Ambrosio-Tortorelli functional. We show that the SL-PAM algorithm is faster than the original PALM algorithm, and leads to competitive denoising, restoration and segmentation results.
Y. Kaloga, M. Foare, N. Pustelnik, and P. Jensen
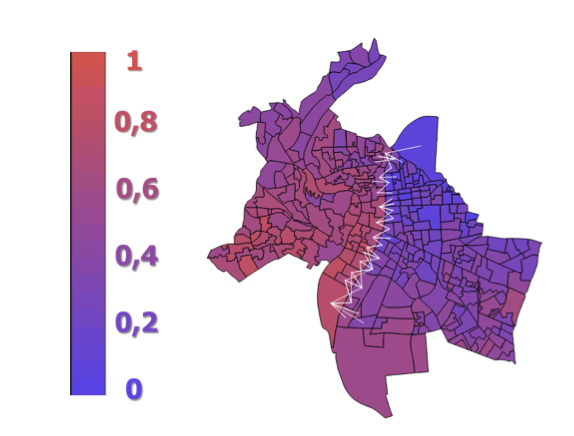
The discrete Mumford-Shah formalism has been introduced for the image denoising problem, allowing to capture both smooth behavior inside an object and sharp transitions on the boundary. In this letter, we propose first to extend this formalism to graphs and to the problem of mixing matrix estimation. New algorithmic schemes with convergence guarantees relying on proximal alternating minimization strategies are derived, and their efficiency (good estimation and robustness to initialization) is evaluated on simulated data, in the context of vote transfer matrix estimation.
